Stock Spinoffs
The Stock Spinoff Index is a list of stocks that have recently completed their spinoff process. Learn more about stock spinoffs below.
| Spinoff Date | Parent Company | Parent Symbol | New Company | New Symbol | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3/20/2024 | Cummins | CMI | Atmus Filtration Tech. | ATMU | Industrials |
| 2/1/2024 | Sodexo | SW | Pluxee | PLX | Industrials |
| 1/3/2024 | FLEX | FLEX | Nextracker | NXT | Industrials |
| 12/1/2023 | Worthington Enterprises | WOR | Worthington Steel | WS | Industrials |
| 11/15/2023 | Alkermes | ALKS | Mural Oncology | MURA | Healthcare |
| 10/17/2023 | Ncr Voyix Corp | VYX | Ncr Atleos Corp | NATL | Insurance |
| 10/4/2023 | Novartis | NVS | Sandoz | SDZNY | Healthcare |
| 10/2/2023 | Kellogg Co. | K | Wk Kellogg Co. | KLG | Consumer Staples |
| 9/28/2023 | Safe & Green Holdings Corp. | SGBX | Safe and Green Development Corp. | SGD | Real Estate |
| 9/8/2023 | LiveOne | LVO | PodcastOne | PODC | Entertainment |
| 8/29/2023 | LICT Corp | LICT | MachTen | MACT | Telecommunications |
| 8/29/2023 | Companhia Brasileira de Distribuição | CBD | Almacenes Exito SA | EXTO | Retail |
| 7/18/2023 | Liberty Media Corp | LSXMA | Atlanta Braves Holdings Inc | BATRK | Media |
| 7/5/2023 | Borgwarner Inc | BWA | Phinia Inc | PHIN | Industrials |
| 7/3/2023 | Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings | LH | Fortrea Holdings Inc | FTRE | Healthcare |
| 6/22/2023 | Imperial Petroleum | IMPP | C3is Inc. | CISS | Industrials |
| 6/1/2023 | Mdu Resources Group Inc | MDU | Knife River Corp. | KNF | Materials |
| 5/24/2023 | Wisekey International Holding SA | WKEY | SEALSQ Corp. | LAES | Technology |
| 5/4/2023 | Johnson & Johnson | JNJ | Kenvue | KVUE | Healthcare |
| 4/21/2023 | Sphere Entertainment Co. | SPHR | Madison Square Garden Entertainment Corp. | MSGE | Communication Services |
| 4/4/2023 | Crane Nxt Co. | CXT | Crane Co. | CR | Industrials |
| 3/31/2023 | Safehold Inc, iStar | SAFE, STAR | Star Holdings | STHO | Real Estate |
| 3/8/2023 | Castor Maritime Inc | CTRM | Toro Corp. | TORO | Industrials |
| 1/17/2023 | Jefferies Financial Group Inc | JEF | Vitesse Energy, Inc | VTS | Energy |
| 1/4/2023 | General Electric Co. | GE | GE Healthcare Technologies Inc. | GEHC | Healthcare |
What is a stock spinoff?
A stock spinoff is a type of corporate action where a parent company separates (spins off) a section of itself into an independent entity.
The process involves distributing shares of the new company to the parent company shareholders.
Generally, the new entity will have its own management structure and a unique corporate identity, but will continue to have a very similar shareholder structure.
Why do stock spinoffs happen?
Companies choose to spin off an asset for various strategic, operational, and financial reasons. The following are some of the most common:
To re-focus on the core business
If you have ever worked in a large company, you know how difficult it can be when the business gets too big and is trying to focus on too many goals simultaneously. Often, one area of the company takes off, and although other areas of the business might be profitable, they simply are taking away focus from the core business.
When this occurs in a public company, the management might decide that spinning off that section of the business into a standalone entity makes more sense. By doing so, it aligns the company to focus on its mission.
Furthermore, it allows the new, independent company to focus on its core business as well.
Unlock hidden value
Sometimes, a company’s stock price does not fully reflect the total value of all its business arms. But, as standalone entities, investors and analysts can better analyze and value the company.
In such cases, a spinoff can help unlock this hidden value. When separated from the parent company, the independent company may receive a higher valuation.
For example, shortly after IPOing in 2002, eBay acquired Paypal for $1.5 billion in stock in a transformational acquisition. Immediately, PayPal became the preferred payment method on eBay, with 1 in 4 transactions occurring via PayPal.
Fast forward to 2013, hundreds of millions of people were using PayPal, accounting for nearly 50% of eBay’s revenue. The company got so big and profitable that activist investors such as Carl Icahn began demanding that PayPal be spun out of eBay to reach its full potential. It was simply too hard for analysts to value one company (eBay) that had two separate arms (marketplace and payment provider).
In July, 2015, PayPal spun off into its own public company to reach its full value potential.
Risk aversion
If an arm of a company contains higher risk, such as regulatory concerns, lawsuit exposure, or just higher general volatility, the parent company may choose to spin that area of the business off.
Not only will spinning off that area of the business benefit the parent company, but it also allows investors to choose which area of the business they would rather hold – the riskier spinoff or, the safer parent.
Pressure from shareholders or activist investors
Just like in our PayPal example above, sometimes companies face pressure from shareholders or activist investors to spin off a division. These shareholders may believe that the company is too complex or that the sum of the parts is greater than the whole.
Tax Benefits:
A spinoff is generally tax-free to the parent company and shareholders. Shareholders only have to pay taxes on the sale of their new shares.
Stock Spinoff Risks
Although spinoffs have been shown to outperform the market, that doesn’t mean that individual separations aren’t without risks. The following risks can impact both the company and its investors:
Management
A company can have the best product or service in the world, but good management is necessary for the company to succeed. With a spinoff being a new, independent company, it is more imperative than ever that it has high-quality management and executives.
Unknown company
Although a spinoff may have some brand recognition, more often than not, it will be significantly less than its parent company’s reputation. This lack of brand recognition can lead to potential cost increases in re-educating the market about the brand and its offerings.
Volatility
A new spinoff’s stock price can have a lot of volatility in the days and weeks after becoming independent. This is generally due to investors wanting to keep a concentrated position in the parent company or looking at new shares as a “dividend” and selling the spinoff regardless of its long-term prospects.
How do spinoffs typically perform in the market?
A recent study from Goldman Sachs analyzing more than 160 corporate separations found that spinoffs outperform their respective sector indexes by 6% during the following two years.
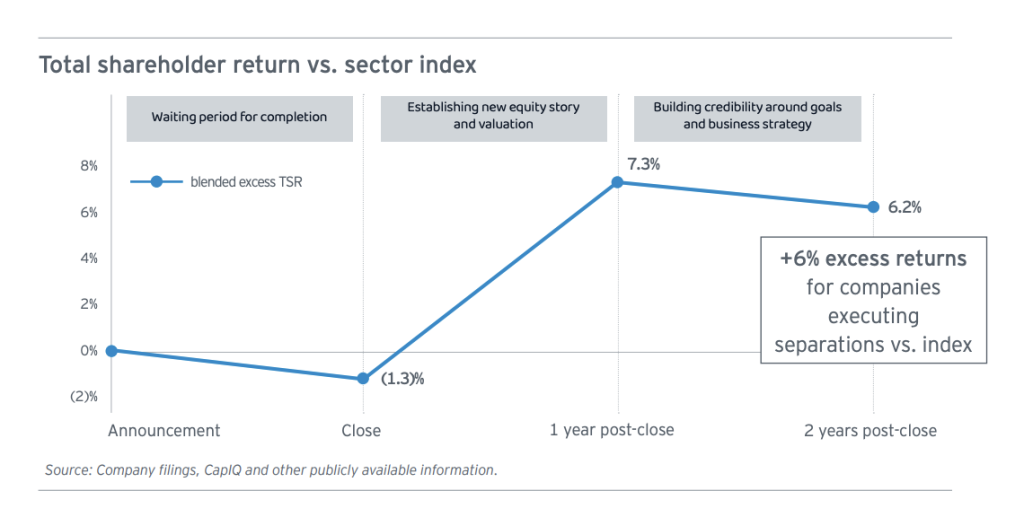
With that being said, though, the aggregate performance of spinoffs, as represented by the CSD ETF, has underperformed. This is primarily due to the bull market in equities and more and more investors becoming aware of the power of spinoffs and thus bringing down aggregate performance.
Although aggregate performance has dropped in recent years, individual spinoffs have performed well. For example, investors who purchased Thungela (TGA) in the spinoff from Anglo American had the potential to 10x their investment in only a year after the spinoff occurred.
Why do spinoffs outperform?
Spinoffs usually outperform the markets due to two main reasons.
Indiscriminate selling leads to good entry points
Because spinoffs are often a significantly smaller subdivision in a much larger conglomerate, investors may be less aware of precisely what the business does or how it makes money.
Often, investors are interested in owning the parent company and view any spinoff as “free money” or a “special dividend .”This viewpoint causes investors to sell, putting pressure on a low-volume trading stock.
Furthermore, large-cap-focused institutions have mandates prohibiting them from owning small-cap stocks, forcing them to sell smaller spinoffs.
Both situations can lead to short-term price disruption and good entry points for investors.
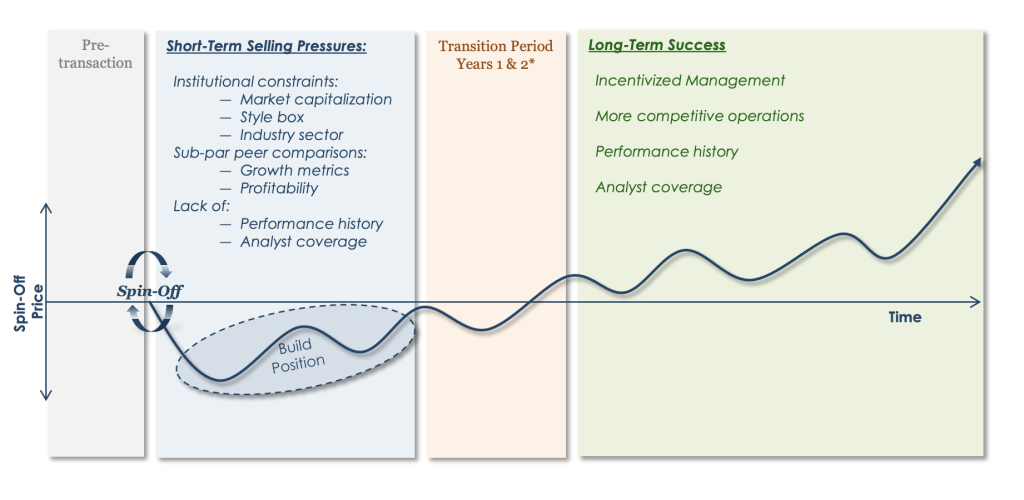
Positive Incentives For the New Management Team and Employees
As a standalone company, the new spinoff often empowers new management’s drive to create value. No longer hampered under the parent company, the spinoff can move quicker and with more focus on its product offerings. Management and employees of spinoffs are also often given stock options in the new company, helping to incentivize them to get the stock’s value up.
How To Invest In Spinoffs
There are two ways to take advantage of stock spinoffs as an investor.
The first is to invest directly in a stock once it announces an upcoming spinoff. In this option, buy shares in the parent company and hold until…
The second and more straightforward way is to purchase a spinoff-focused ETF such as the Invesco S&P Spinoff ETF (CSD). Institutional investors – with a $1 million minimum investment – can buy the Kinetics Spinoff and Corporate Restructuring Fund (LSHUX).
Stock Spinoff Example
On July 27, 1995, the Anheuser-Busch Companies announced they would spin off their subsidiary, Campbell Taggart Inc, the nation’s second-largest bakery. As a subsidiary of the world’s largest brewer, Campbell-Taggart was being ignored and mismanaged to the point that it was unprofitable.
In 1996, a tax-free spinoff occurred with Campbell Taggart being renamed The Earthgrains Company. Once the company was out of the constraints of its parent company, Earthgrains began to grow significantly. At the time of the spinoff in 1996, Earthgrains’ market cap was $289 million. By 2001 the company was sold to Sara Lee Corp. for $1.8 billion – a 44% annualized return in five years.
How to track upcoming spinoffs?
When a publicly traded company wants to issue new stock through a spinoff, it must file a 10-12B form with the SEC.
A 10-12B form generally contains information from the parent company to its shareholders explaining why the spinoff makes sense, how the company would have performed in the past as an independent entity, how it will perform going forward, and any further outlook.
You can find 10-12B forms on the SEC website here.
FAQ:
Are there specific sectors or countries where spinoffs are more common?
According to research from Goldman Sachs, the industrials sector represented more than 30% of spinoffs in 2022.
| Sector | Transaction % in 2022 |
| Industrials | 31% |
| Technology, media, & telecommunications | 18% |
| Consumer | 14% |
| Natural Resources | 13% |
| Healthcare | 11% |
| Financial | 8% |
| Real Estate | 5% |
In 2022, the United States represented 69% of all spinoffs.
Are there any tax implications with stock spinoffs?
Tax implications vary depending on the spinoff and the investor’s tax jurisdiction. In some cases, the receipt of shares in the spinoff may be tax-free to shareholders, but this depends on the specific structure of the transaction.
How long do spinoffs usually take?
Spinoffs, on average, take around 11 months to occur from the announcement date.
Research, though, has shown that there is no correlation between the amount of time it takes for a spinoff to occur and its ultimate stock performance.
Can a spinoff ever be reversed or reabsorbed into the parent company?
While it’s not common, it is possible for a spun-off entity to be reabsorbed or reacquired by the parent company or another company, particularly in scenarios where the spun-off company struggles to operate independently.